Project Description
Internal physiological stress is actually more commonly referred to as “psychological or emotional stress.” This type of stress is related to feeling a kind of pressure in our brains and emotional states. For example, internal situations like thinking about something, worrying, or putting pressure on ourselves can trigger this stress.
Imagine you’re studying to pass an exam and you feel anxious about it. This is an example of internal physiological stress. In this situation, your brain and body try to prepare themselves to cope with the exam, leading to an increase in your heart rate, the release of stress hormones, and tension in your muscles.
Some positive effects when internal stress decreases:
- Emotional Well-being: Reducing internal stress can positively affect emotional well-being. It can bring about better emotional balance, happiness, and a sense of peace.
- Physical Health Improvement: Chronic stress can contribute to physical health problems. Reducing internal stress can alleviate these negative effects and improve overall health.
- Better Concentration and Performance: Lower stress levels can enhance a person’s ability to focus mentally, improve concentration, and allow for better performance in tasks or work.
- Good Sleep Quality: Decreasing internal stress can improve sleep quality. Better sleep has a positive impact on overall health and well-being.
Some things that can be done to reduce internal stress:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can reduce stress and improve overall health.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Taking deep breaths can reduce stress responses in the body and help with relaxation.
- Meditation and Yoga: These practices can enhance mental and emotional balance and reduce stress.
- Social Support: Getting support from family, friends, or professionals can help cope with internal stress.
- Time Management: Organizing tasks and managing time effectively can reduce internal stress.
- Hobbies and Activities: Spending time on personal interests, enjoying oneself, and relaxing can reduce internal stress.
The Impact of Internal Physiological Stress on Hormones:
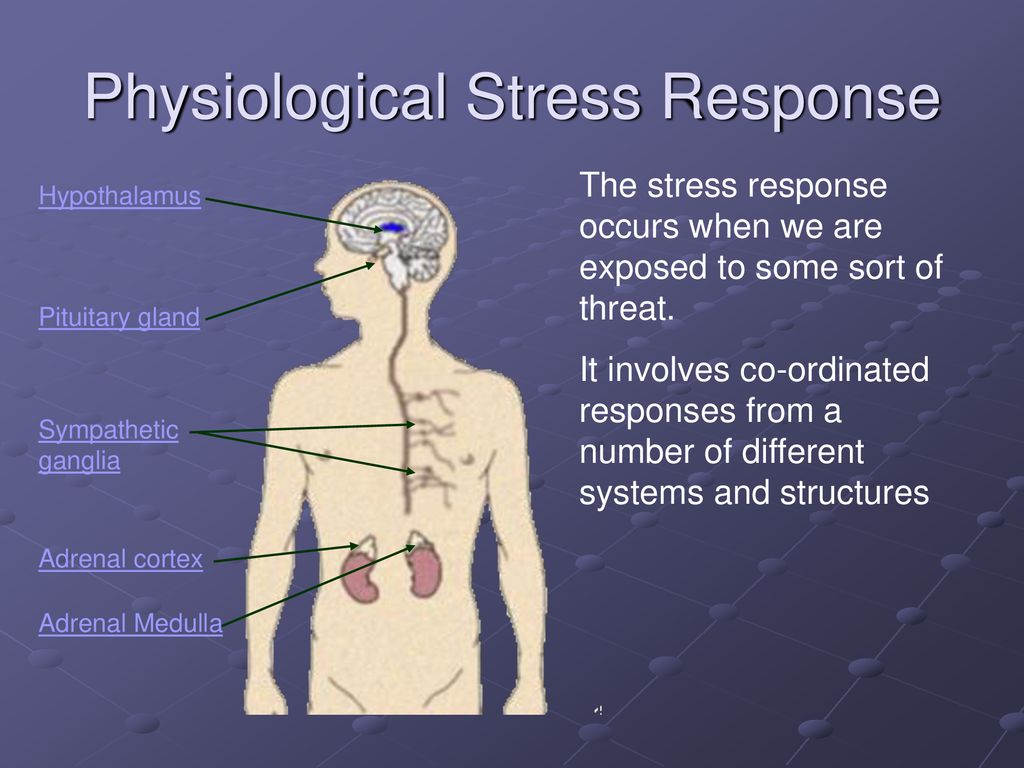
Internal physiological stress triggers a biological response known as the “fight or flight” response in the body. When faced with stress, the pituitary gland in the brain sends signals to the adrenal glands. These glands release stress hormones like adrenaline and noradrenaline. These hormones increase heart rate, raise blood pressure, and release energy sources.
Additionally, cortisol hormone supports energy production by increasing glucose release in the liver. However, in prolonged stress situations, consistently high levels of stress hormones can lead to health problems. Coping strategies for stress can help balance these hormonal changes and reduce their long-term negative effects.